Update on 01/06/2021: Added links to some helpful articles.
Laravel Sanctum is a slim authentication system for Single Page Applications that don't need the full-meal-deal of an OAuth2 implementation. Sanctum protects an API from Cross Site Forgery Requests by setting a browser cookie and checking for the cookie (or token) on request to ensure requests are coming from approved requesters, be it a first-party SPA or mobile application. It should be paired with a user authentication system.
The majority of this article is a concise summary of what's in the official documentation. If you need more details, follow the link below.
Official Documentation: https://laravel.com/docs/8.x/sanctum
Other helpful sources:
Quotes from the Docs
"Laravel Sanctum provides a featherweight authentication system for SPAs (single page applications), mobile applications, and simple, token based APIs."
"Laravel Sanctum is only concerned with managing API tokens and authenticating existing users using session cookies or tokens. Sanctum does not provide any routes that handle user registration, password reset, etc."
"When Sanctum examines an incoming HTTP request, it will first check for an authentication cookie and, if none is present, Sanctum will then examine the Authorization header for a valid API token."
Installation
Go to the project folder in terminal and add the Sanctum package with composer.
composer require laravel/sanctum
Publish the config and migration files.
php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Laravel\Sanctum\SanctumServiceProvider"
Then run migrations.
php artisan migrate
Config for SPA Authentication
Sanctum uses Laravel's built-in cookie based session authentication services. You get CSRF protection, session auth, and leakage protection of auth credentials via XSS.
Note! Because using cookies, SPA and API must share the same TLD but can be on separate subdomains.
First Party Domains
Decide what domain(s) the SPA will be making requests from using stateful config in config/sanctum.php or set as SANCTUM_STATEFUL_DOMAINS in .env[.local]
The Sanctum config file accepts a comma-separated list of domains. Include port numbers, if required!
"Stateful" means the cookies will be set for these domains. If the cookie exists, the SPA is authenticated. The session cookie being stored in the browser signifies the app knows the user is logged in and can retrieve information about the logged in user. A "stateless" system would require a token to be passed to the API on every single request.
Add Middleware
Add EnsureFrontendRequestsAreStateful::class, to api middleware group in app/Http/Kernel.php file.
CORS & Cookies
Update supports_credentials to true in config/cors.php file. This ensures the applications CORS configuration is returning the Access-Control-Allow-Credentials header with a value of True.
More on CORS: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CORS
Gotcha: One thing to note, which tripped me up for a bit. When requesting a cookie from /sanctum/csrf-cookie from a domain other than the API, ensure you set "credentials" : "include" or the cookie won't be saved to browser storage.
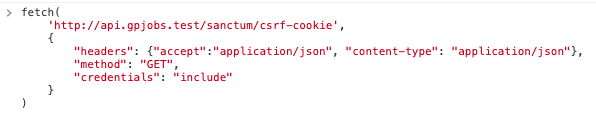
Axios make this easy with the following global configuration.
axios.defaults.withCredentials = true;
Lastly, update sessions cookie domain config in config/session.php or .env to allow subdomains.
'domain' => '.domain.com',
Protecting Routes
Attach the sanctum authentication guard to API routes in the routes/api.php file. All requests to these routes require the X-XSRF-TOKEN header or a valid API token header.
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
Route::middleware('auth:sanctum')->get('/user', function (Request $request) {
return $request->user();
});
Authenticating
CSRF
To authenticate the SPA, the "login" page should first make a request to /sanctum/csrf-cookie endpoint to initialize. This sets an XSRF-TOKEN cookie, which should be passed in an X-XSRF-TOKEN header on subsequent requests.
axios.get('/sanctum/csrf-cookie').then(response => {
// Login...
});
Logging In
Now a POST request to /login can be implemented.
If successful, subsequent requests to application routes will be automatically authenticated via the session cookie that the Laravel app issued to the client.
If the users' session expires due to lack of activity and a 401 or 419 HTTP response is received, redirect to /login.
Next Up
This is only step one. Now to configure user token authentication with Laravel Fortify a custom implementation.